Quantile Chart
Quantile Chart - It can also refer to dividing a probability. Find the quantiles of the normal distribution. Quartiles are a type of quantile. Quantiles split data or distributions into equal parts to better understand the data's position. In essence, quantiles are points in a dataset that help to understand the distribution. Essentially, if you have a dataset, a quantile generates segments. Here’s a simple definition of each: Discover how it is calculated through examples. It helps in understanding the distribution of data. In statistics and probability, quantiles are cut points dividing the range of a probability distribution into continuous intervals with equal probabilities or dividing the observations in a sample in the. It can also refer to dividing a probability. Common types of quantiles include: Here’s a simple definition of each: Quartiles are three values that split sorted data into four parts, each with an equal number of observations. Also known as q1, or. Quantiles help describe the distribution of values by indicating where data fall relative to the entire dataset. Three terms that students often confuse in statistics are percentiles, quartiles, and quantiles. Find the quantiles of the normal distribution. Discover how it is calculated through examples. Learn how the quantile of a distribution is defined. It can also refer to dividing a probability. It helps in understanding the distribution of data. Here’s a simple definition of each: Common types of quantiles include: Learn how the quantile of a distribution is defined. Here’s a simple definition of each: Quantiles help describe the distribution of values by indicating where data fall relative to the entire dataset. In statistics and probability, quantiles are cut points dividing the range of a probability distribution into continuous intervals with equal probabilities or dividing the observations in a sample in the. Discover how it is calculated through examples.. It can also refer to dividing a probability. Quartiles are three values that split sorted data into four parts, each with an equal number of observations. Quartiles are a type of quantile. Quantiles split data or distributions into equal parts to better understand the data's position. Learn how the quantile of a distribution is defined. Here’s a simple definition of each: In statistics and probability, quantiles are cut points dividing the range of a probability distribution into continuous intervals with equal probabilities or dividing the observations in a sample in the. Quantiles split data or distributions into equal parts to better understand the data's position. In essence, quantiles are points in a dataset that help. Also known as q1, or. Three terms that students often confuse in statistics are percentiles, quartiles, and quantiles. In essence, quantiles are points in a dataset that help to understand the distribution. Find the quantiles of the normal distribution. In statistics and probability, quantiles are cut points dividing the range of a probability distribution into continuous intervals with equal probabilities. Also known as q1, or. Learn how the quantile of a distribution is defined. In statistics and probability, quantiles are cut points dividing the range of a probability distribution into continuous intervals with equal probabilities or dividing the observations in a sample in the. Find the quantiles of the normal distribution. Quantiles help describe the distribution of values by indicating. Common types of quantiles include: Also known as q1, or. Find the quantiles of the normal distribution. Quantiles help describe the distribution of values by indicating where data fall relative to the entire dataset. Quantiles split data or distributions into equal parts to better understand the data's position. In statistics and probability, quantiles are cut points dividing the range of a probability distribution into continuous intervals with equal probabilities or dividing the observations in a sample in the. Range from 0 to 100. Discover how it is calculated through examples. Find the quantiles of the normal distribution. Quantiles help describe the distribution of values by indicating where data. It can also refer to dividing a probability. Also known as q1, or. Learn how the quantile of a distribution is defined. Find the quantiles of the normal distribution. It helps in understanding the distribution of data. In essence, quantiles are points in a dataset that help to understand the distribution. Common types of quantiles include: Also known as q1, or. Here’s a simple definition of each: Quantiles help describe the distribution of values by indicating where data fall relative to the entire dataset. Range from 0 to 100. Find the quantiles of the normal distribution. Quartiles are a type of quantile. It helps in understanding the distribution of data. Discover how it is calculated through examples. Learn how the quantile of a distribution is defined. It can also refer to dividing a probability. Essentially, if you have a dataset, a quantile generates segments.Quartiles & Quantiles Calculation, Definition & Interpretation
Quantiles and Percentiles, Clearly Explained!!! YouTube
Model quality, parameter estimates, and predicted by observed
R QuantileQuantile (QQ) Plot Base Graph Learn By Example
PPT Introduction to Statistics PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1282507
Quantiles are key to understand probability distributions Towards Data Science
The quantilequantile scatter plot of predicted versus observed... Download Scientific Diagram
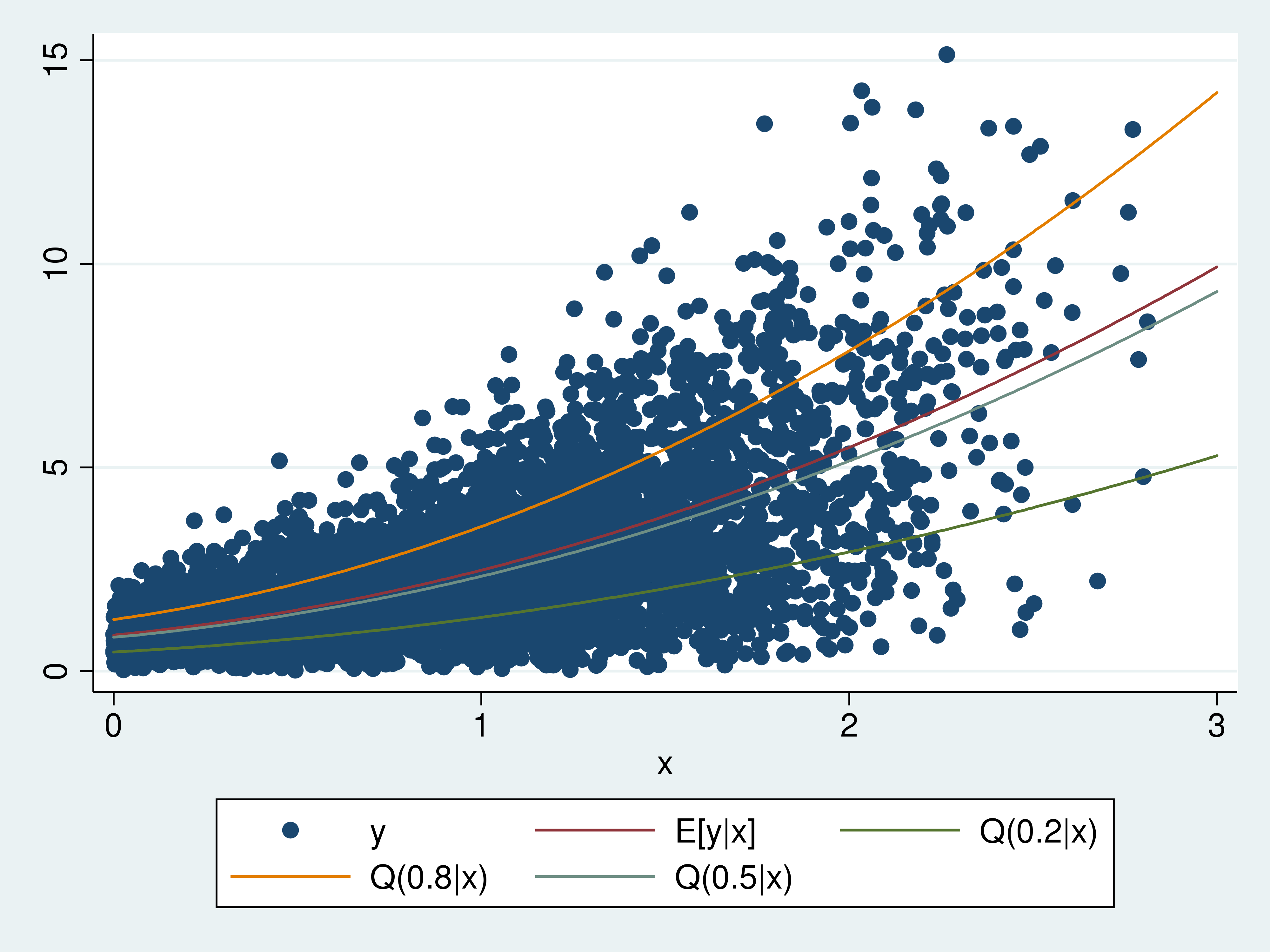
The Stata Blog » Quantile regression allows covariate effects to differ by quantile
Lexile And Quantile Chart
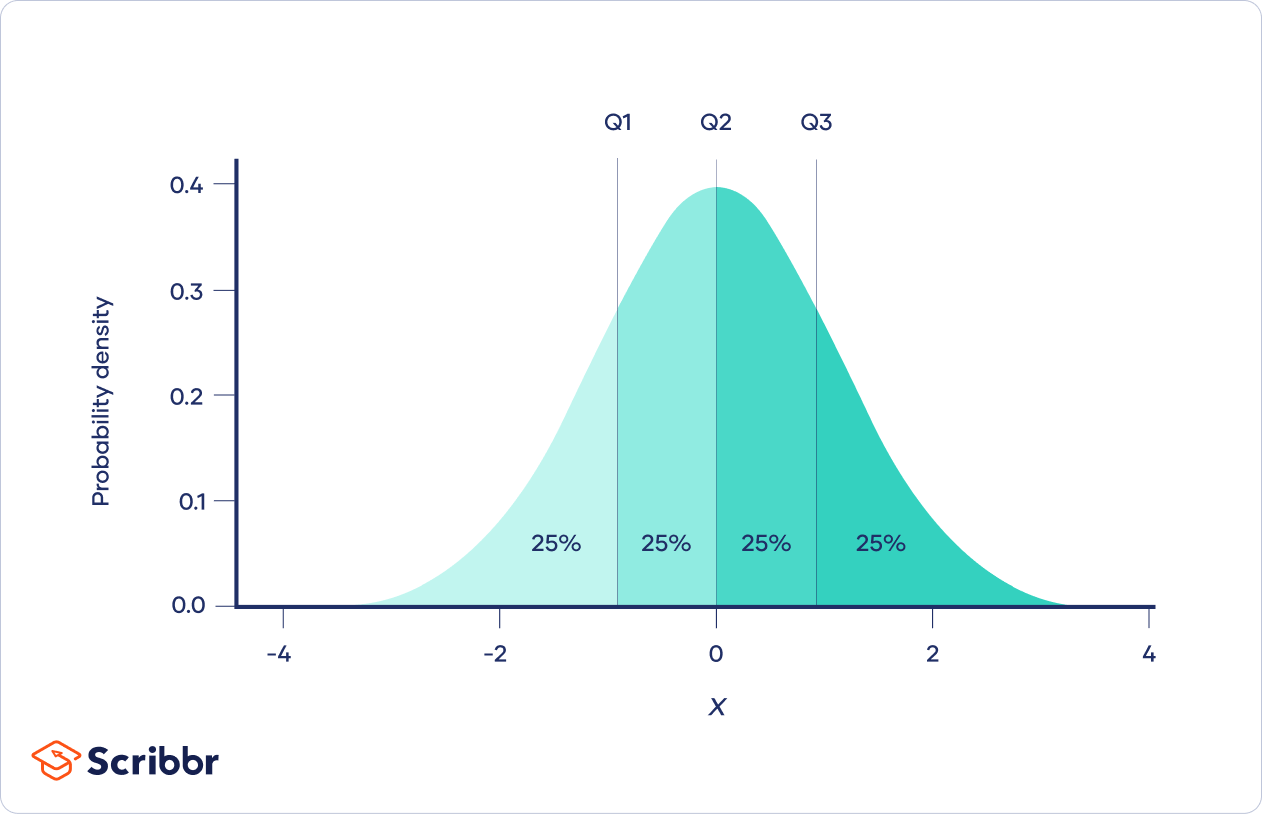
Quantiles Split Data Or Distributions Into Equal Parts To Better Understand The Data's Position.
Quartiles Are Three Values That Split Sorted Data Into Four Parts, Each With An Equal Number Of Observations.
Three Terms That Students Often Confuse In Statistics Are Percentiles, Quartiles, And Quantiles.
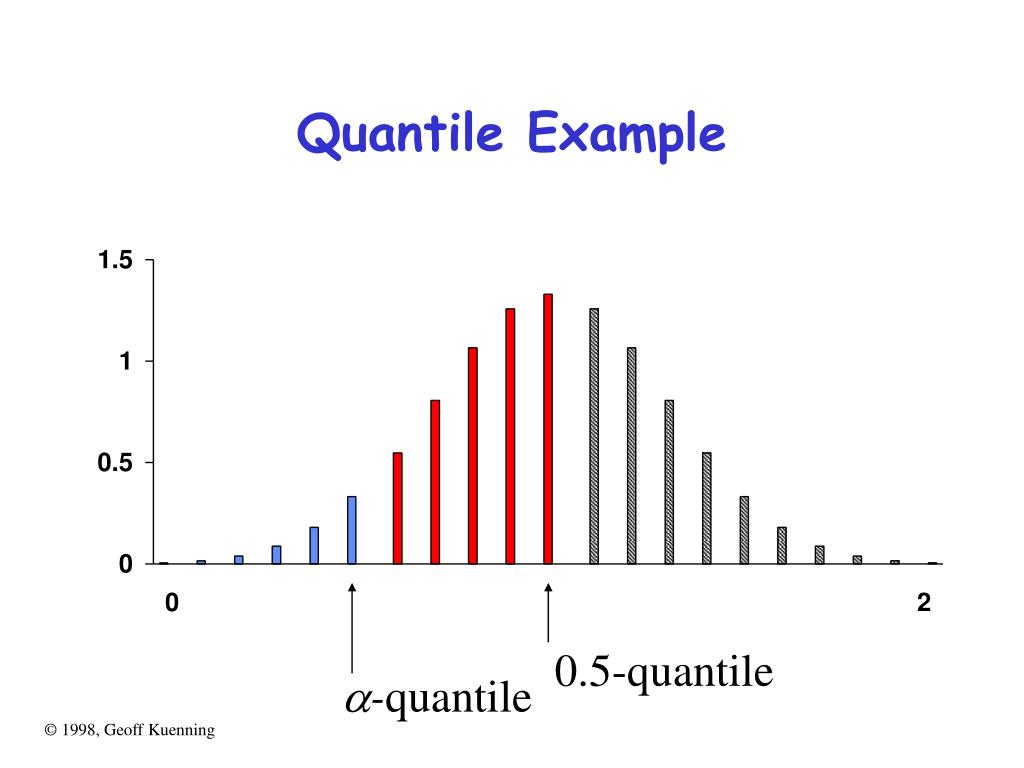
In Statistics And Probability, Quantiles Are Cut Points Dividing The Range Of A Probability Distribution Into Continuous Intervals With Equal Probabilities Or Dividing The Observations In A Sample In The.
Related Post: