Hyperbilirubinemia Newborn Chart
Hyperbilirubinemia Newborn Chart - Explain how to differentiate unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia from conjugated hyperbilirubinemia. Your body breaks down too many red blood cells too fast. Severe hyperbilirubinemia can cause kernicterus, a type of brain damage that leads to movement problems (cerebral palsy) and hearing loss. Low levels of bilirubin in the. Bilirubin is a yellowish substance in your blood. Bilirubin might build up in your blood if: Hyperbilirubinemia is a clinical condition describing an elevation of blood bilirubin level due to the inability to properly metabolise or excrete bilirubin, a product of erythrocytes breakdown. Jaundice makes the skin and the whites of the eyes appear yellow,. Jaundice and asymptomatic hyperbilirubinemia are common clinical problems that can be caused by a variety of disorders, including bilirubin overproduction, impaired bilirubin. High levels of bilirubin in the blood is known as hyperbilirubinemia. Explain how to differentiate unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia from conjugated hyperbilirubinemia. Describe the physiology of bilirubin metabolism. What causes high bilirubin levels (hyperbilirubinemia)? Elevated bilirubin levels can cause jaundice. High levels of bilirubin in the blood is known as hyperbilirubinemia. Your body breaks down too many red blood cells too fast. Key points about hyperbilirubinemia in the newborn hyperbilirubinemia happens when there is too much bilirubin in your baby’s blood. Bilirubin forms when red blood cells break down at the end. A high bilirubin level, or hyperbilirubinemia, occurs when bilirubin has accumulated in your body in excessive amounts. Jaundice and asymptomatic hyperbilirubinemia are common clinical problems that can be caused by a variety of disorders, including bilirubin overproduction, impaired bilirubin. What causes high bilirubin levels (hyperbilirubinemia)? Describe the physiology of bilirubin metabolism. It forms after red blood cells break down and travel through your liver, gallbladder, and digestive tract before excretion. Your body breaks down too many red blood cells too fast. Hyperbilirubinemia is a clinical condition describing an elevation of blood bilirubin level due to the inability to properly. It forms after red blood cells break down and travel through your liver, gallbladder, and digestive tract before excretion. Bilirubin forms when red blood cells break down at the end. High levels of bilirubin in the blood is known as hyperbilirubinemia. Low levels of bilirubin in the. Severe hyperbilirubinemia can cause kernicterus, a type of brain damage that leads to. It forms after red blood cells break down and travel through your liver, gallbladder, and digestive tract before excretion. Hyperbilirubinemia is a clinical condition describing an elevation of blood bilirubin level due to the inability to properly metabolise or excrete bilirubin, a product of erythrocytes breakdown. Hyperbilirubinemia is a condition in which there is a build up of bilirubin in. Describe the physiology of bilirubin metabolism. Jaundice makes the skin and the whites of the eyes appear yellow,. Jaundice and asymptomatic hyperbilirubinemia are common clinical problems that can be caused by a variety of disorders, including bilirubin overproduction, impaired bilirubin. Key points about hyperbilirubinemia in the newborn hyperbilirubinemia happens when there is too much bilirubin in your baby’s blood. Severe. Jaundice makes the skin and the whites of the eyes appear yellow,. Hyperbilirubinemia is a condition in which there is a build up of bilirubin in the blood, causing yellow discoloration of the eyes and skin, called jaundice. Low levels of bilirubin in the. Explain how to differentiate unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia from conjugated hyperbilirubinemia. A high bilirubin level, or hyperbilirubinemia, occurs. What causes high bilirubin levels (hyperbilirubinemia)? It forms after red blood cells break down and travel through your liver, gallbladder, and digestive tract before excretion. High levels of bilirubin in the blood is known as hyperbilirubinemia. Hyperbilirubinemia is a clinical condition describing an elevation of blood bilirubin level due to the inability to properly metabolise or excrete bilirubin, a product. Bilirubin is a yellowish substance in your blood. Severe hyperbilirubinemia can cause kernicterus, a type of brain damage that leads to movement problems (cerebral palsy) and hearing loss. Your body breaks down too many red blood cells too fast. Jaundice makes the skin and the whites of the eyes appear yellow,. Explain how to differentiate unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia from conjugated hyperbilirubinemia. Severe hyperbilirubinemia can cause kernicterus, a type of brain damage that leads to movement problems (cerebral palsy) and hearing loss. Bilirubin might build up in your blood if: Jaundice makes the skin and the whites of the eyes appear yellow,. It forms after red blood cells break down and travel through your liver, gallbladder, and digestive tract before excretion. Bilirubin. Explain how to differentiate unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia from conjugated hyperbilirubinemia. Key points about hyperbilirubinemia in the newborn hyperbilirubinemia happens when there is too much bilirubin in your baby’s blood. What causes high bilirubin levels (hyperbilirubinemia)? Severe hyperbilirubinemia can cause kernicterus, a type of brain damage that leads to movement problems (cerebral palsy) and hearing loss. High levels of bilirubin in the. Jaundice makes the skin and the whites of the eyes appear yellow,. Bilirubin is a yellowish substance in your blood. High levels of bilirubin in the blood is known as hyperbilirubinemia. Bilirubin forms when red blood cells break down at the end. Severe hyperbilirubinemia can cause kernicterus, a type of brain damage that leads to movement problems (cerebral palsy) and. What causes high bilirubin levels (hyperbilirubinemia)? Low levels of bilirubin in the. Your body breaks down too many red blood cells too fast. Key points about hyperbilirubinemia in the newborn hyperbilirubinemia happens when there is too much bilirubin in your baby’s blood. Describe the physiology of bilirubin metabolism. Bilirubin might build up in your blood if: Elevated bilirubin levels can cause jaundice. Severe hyperbilirubinemia can cause kernicterus, a type of brain damage that leads to movement problems (cerebral palsy) and hearing loss. Jaundice makes the skin and the whites of the eyes appear yellow,. A high bilirubin level, or hyperbilirubinemia, occurs when bilirubin has accumulated in your body in excessive amounts. Hyperbilirubinemia is a condition in which there is a build up of bilirubin in the blood, causing yellow discoloration of the eyes and skin, called jaundice. It forms after red blood cells break down and travel through your liver, gallbladder, and digestive tract before excretion. Bilirubin forms when red blood cells break down at the end. Bilirubin is a yellowish substance in your blood.Bilirubin Level For 7 Days Baby Chart Jaundice Chart Newborn
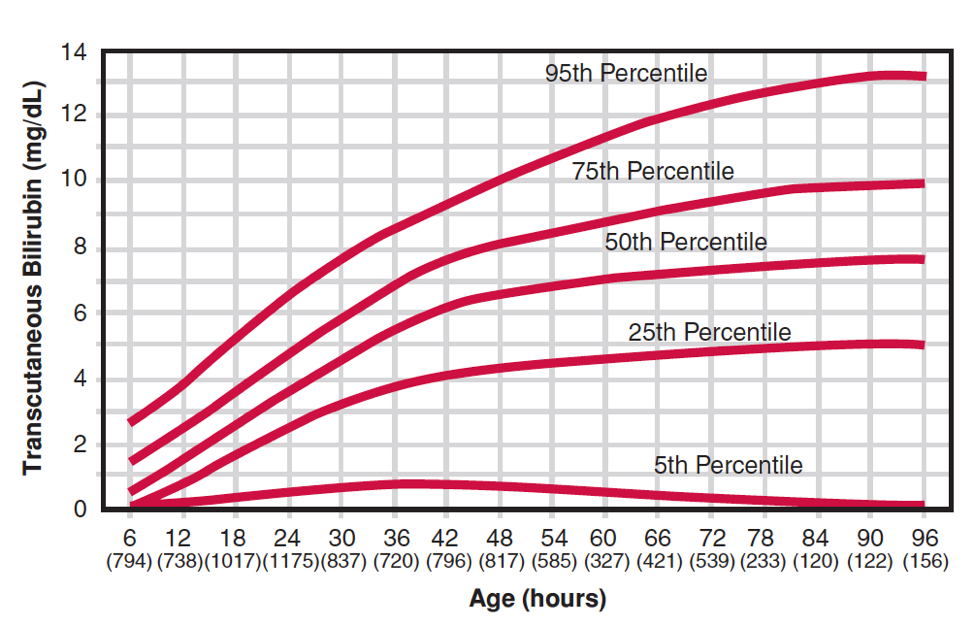
Neonatal Bilirubin Levels
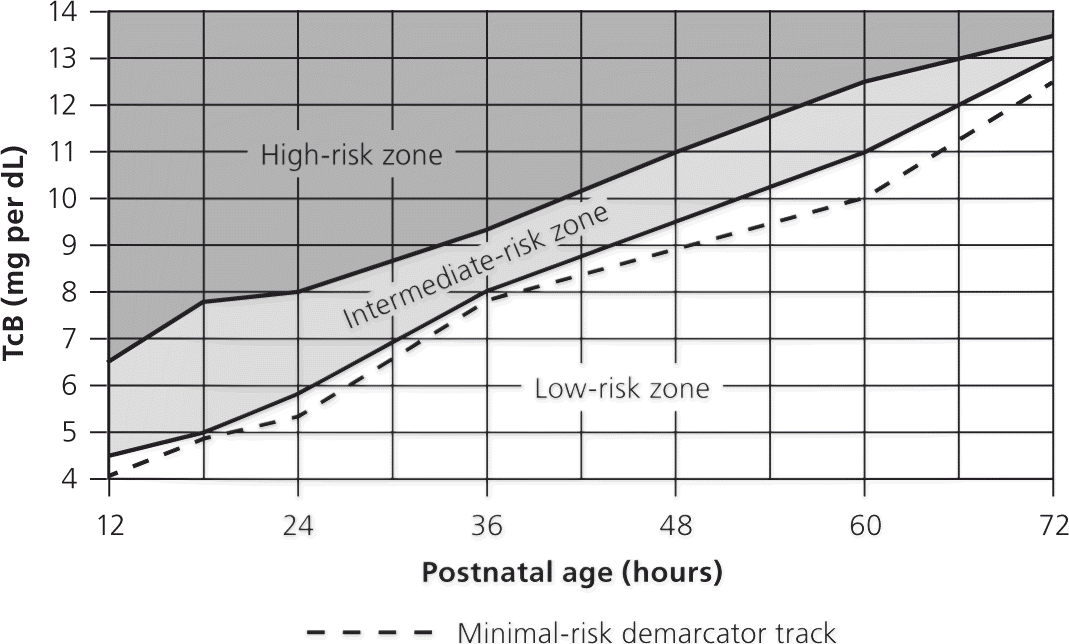
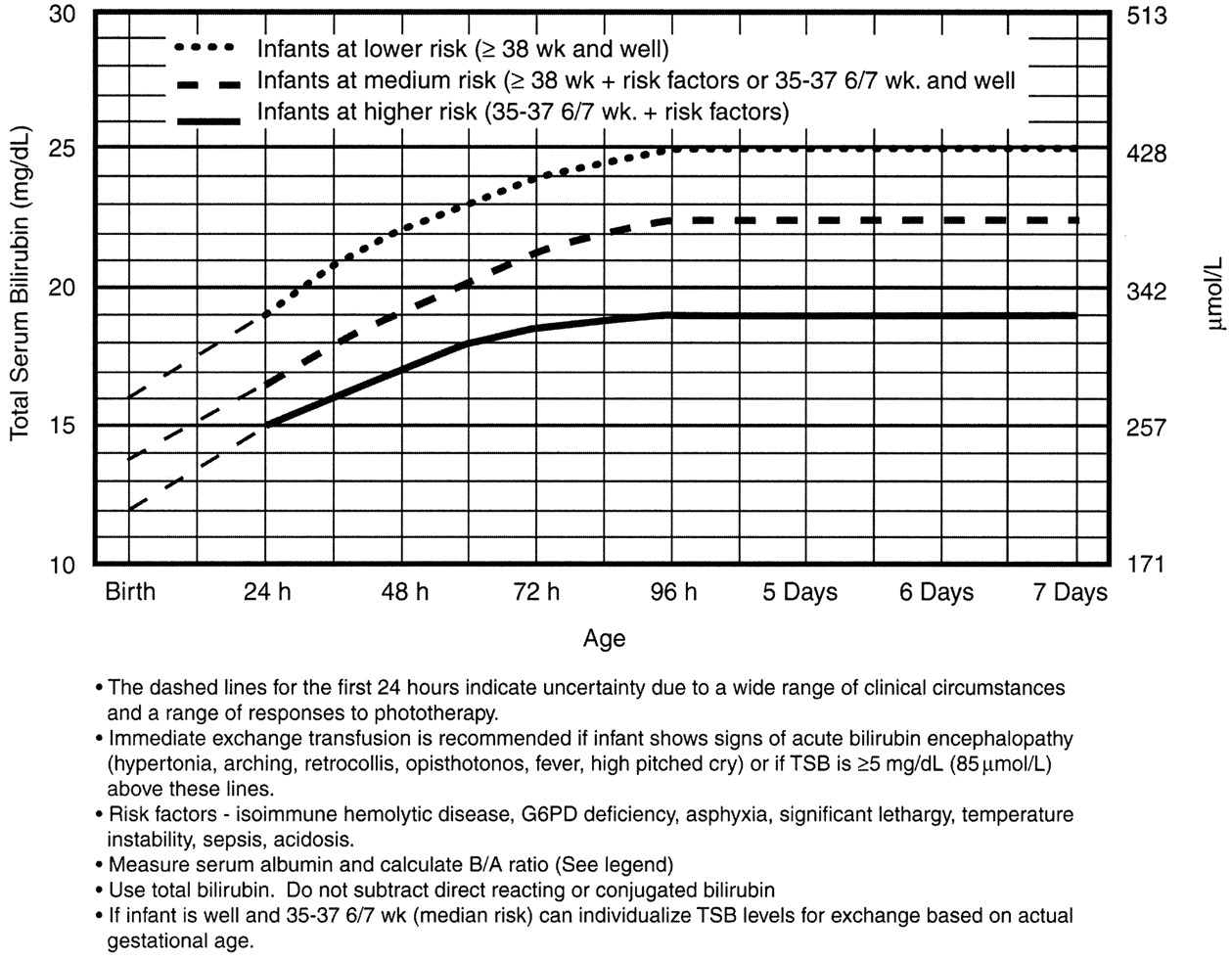
Evaluation and Treatment of Neonatal Hyperbilirubinemia AAFP
Neonatal Bilirubin Level Chart Hyperbilirubinemia Infant
Nice Guidelines Bilirubin Chart Clinical Practice Guidelines Jaundice Flowchart
Neonatal Jaundice Bilirubin Levels Chart 5 Kramer Scale Jaundice In Newborn Bilirubin Level Chart
Bilirubin types, bilirubin levels chart and causes of high bilirubin levels
05.Neonatal hyperbilirubinemia CLINICAL PEDIATRIC HEPATOLOGY
Chart For Bilirubin Levels In Newborns Bilirubin Level Chart
Jaundice charts Neonatal resources Clinicians Tools and Resources QUICK LINK Flourish
High Levels Of Bilirubin In The Blood Is Known As Hyperbilirubinemia.
Explain How To Differentiate Unconjugated Hyperbilirubinemia From Conjugated Hyperbilirubinemia.
Hyperbilirubinemia Is A Clinical Condition Describing An Elevation Of Blood Bilirubin Level Due To The Inability To Properly Metabolise Or Excrete Bilirubin, A Product Of Erythrocytes Breakdown.
Jaundice And Asymptomatic Hyperbilirubinemia Are Common Clinical Problems That Can Be Caused By A Variety Of Disorders, Including Bilirubin Overproduction, Impaired Bilirubin.
Related Post: