Glucose A1C Conversion Chart
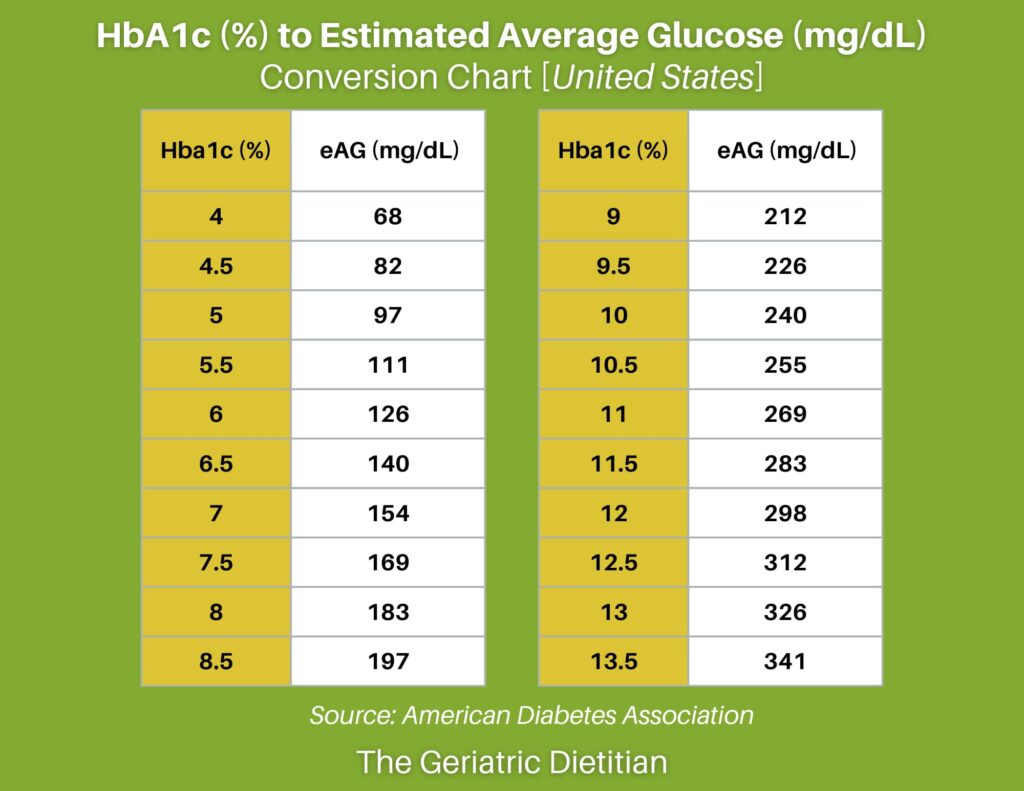
Glucose A1C Conversion Chart - Glucose is a sugar necessary for energy production and the correct functioning of many organs in the body. Glucose is a monosaccharide containing six carbon atoms and an aldehyde group, and is therefore an aldohexose. Checking your blood glucose will tell you whether you’re reaching your blood glucose targets. Blood glucose, or blood sugar, is the main sugar found in your blood. Your body breaks down most. If your blood sugar levels dip too low (hypoglycemia) or grow too high (hyperglycemia), they can affect your. Carbohydrates are ubiquitous energy sources for every organism worldwide and are essential. You know the term glucose, but exactly what does glucose do? “sweet”) has the molecular formula c 6 h 12. Learn how your body uses glucose and what happens if your blood glucose levels are too high, how it's made and how it is consumed by the body Glucose is a sugar necessary for energy production and the correct functioning of many organs in the body. Learn more about glucose function, how the body uses glucose (sugar), and how glucose works to provide energy. You get it mainly from carbohydrates that you eat, like sugar and grains. It is carried through your blood to the cells in your body,. Glucose, one of a group of carbohydrates known as simple sugars (monosaccharides). You know the term glucose, but exactly what does glucose do? Your body breaks down most. Carbohydrates are ubiquitous energy sources for every organism worldwide and are essential. “sweet”) has the molecular formula c 6 h 12. But blood glucose that’s too high or too low can be harmful. Your body breaks down most. There are 2 ways to do it. If your blood sugar levels dip too low (hypoglycemia) or grow too high (hyperglycemia), they can affect your. Glucose is the body’s main source of energy. Learn how your body uses glucose and what happens if your blood glucose levels are too high, how it's made and how. There are 2 ways to do it. • use a blood glucose meter to learn what your blood glucose is at. Your body breaks down most. If your blood sugar levels dip too low (hypoglycemia) or grow too high (hyperglycemia), they can affect your. Glucose is the body’s main source of energy. Glucose is the body’s main source of energy. Learn how your body uses glucose and what happens if your blood glucose levels are too high, how it's made and how it is consumed by the body There are 2 ways to do it. “sweet”) has the molecular formula c 6 h 12. Glucose is a sugar necessary for energy production. Glucose is the body’s main source of energy. There are 2 ways to do it. It comes from the food you eat. Glucose, one of a group of carbohydrates known as simple sugars (monosaccharides). Glucose is a sugar necessary for energy production and the correct functioning of many organs in the body. Glucose, one of a group of carbohydrates known as simple sugars (monosaccharides). Learn how your body uses glucose and what happens if your blood glucose levels are too high, how it's made and how it is consumed by the body It comes from the food you eat. Carbohydrates are ubiquitous energy sources for every organism worldwide and are essential. Your. • use a blood glucose meter to learn what your blood glucose is at. There are 2 ways to do it. Checking your blood glucose will tell you whether you’re reaching your blood glucose targets. Glucose is a monosaccharide containing six carbon atoms and an aldehyde group, and is therefore an aldohexose. If your blood sugar levels dip too low. “sweet”) has the molecular formula c 6 h 12. If your blood sugar levels dip too low (hypoglycemia) or grow too high (hyperglycemia), they can affect your. Glucose is a monosaccharide containing six carbon atoms and an aldehyde group, and is therefore an aldohexose. Glucose, one of a group of carbohydrates known as simple sugars (monosaccharides). Blood glucose, or blood. Checking your blood glucose will tell you whether you’re reaching your blood glucose targets. Glucose is the body’s main source of energy. “sweet”) has the molecular formula c 6 h 12. If your blood sugar levels dip too low (hypoglycemia) or grow too high (hyperglycemia), they can affect your. Your body breaks down most. Glucose is a sugar necessary for energy production and the correct functioning of many organs in the body. Glucose, or blood sugar, is a type of simple carbohydrate. You get it mainly from carbohydrates that you eat, like sugar and grains. If your blood sugar levels dip too low (hypoglycemia) or grow too high (hyperglycemia), they can affect your. There. Checking your blood glucose will tell you whether you’re reaching your blood glucose targets. Glucose is a sugar necessary for energy production and the correct functioning of many organs in the body. Carbohydrates are ubiquitous energy sources for every organism worldwide and are essential. If your blood sugar levels dip too low (hypoglycemia) or grow too high (hyperglycemia), they can. Glucose, or blood sugar, is a type of simple carbohydrate. Glucose, one of a group of carbohydrates known as simple sugars (monosaccharides). It is carried through your blood to the cells in your body,. But blood glucose that’s too high or too low can be harmful. It is your body's primary source of energy. Blood glucose, or blood sugar, is the main sugar found in your blood. Your body breaks down most. Checking your blood glucose will tell you whether you’re reaching your blood glucose targets. Learn how your body uses glucose and what happens if your blood glucose levels are too high, how it's made and how it is consumed by the body You get it mainly from carbohydrates that you eat, like sugar and grains. Learn more about glucose function, how the body uses glucose (sugar), and how glucose works to provide energy. You know the term glucose, but exactly what does glucose do? Glucose is a monosaccharide containing six carbon atoms and an aldehyde group, and is therefore an aldohexose. If your blood sugar levels dip too low (hypoglycemia) or grow too high (hyperglycemia), they can affect your. • use a blood glucose meter to learn what your blood glucose is at. “sweet”) has the molecular formula c 6 h 12.A1c To Blood Glucose Conversion Chart A1c Vs Glucose Levels
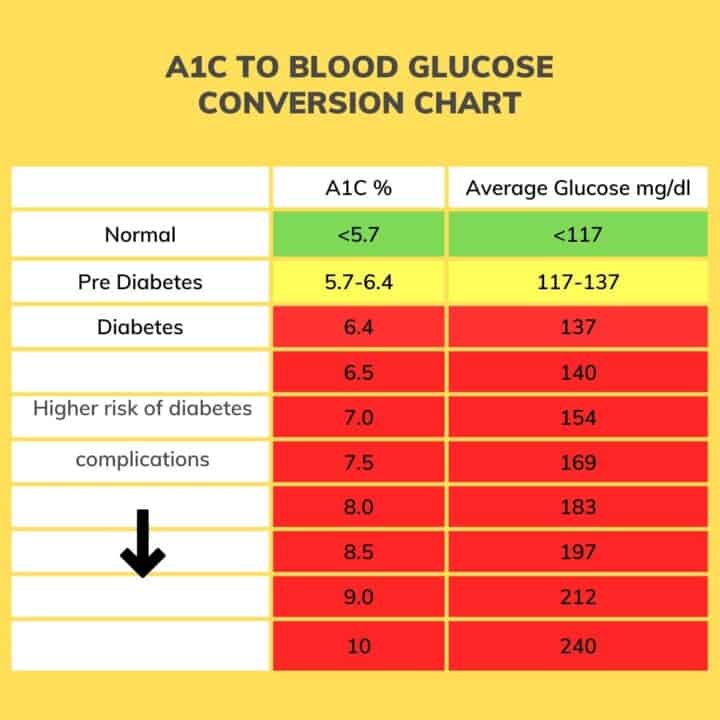
A1c To Blood Glucose Conversion Chart
A1c Glucose Conversion Chart
Conversion Chart For A1c A1c Chart Diabetes Printable Calcul
Blood Glucose A1c Conversion Chart
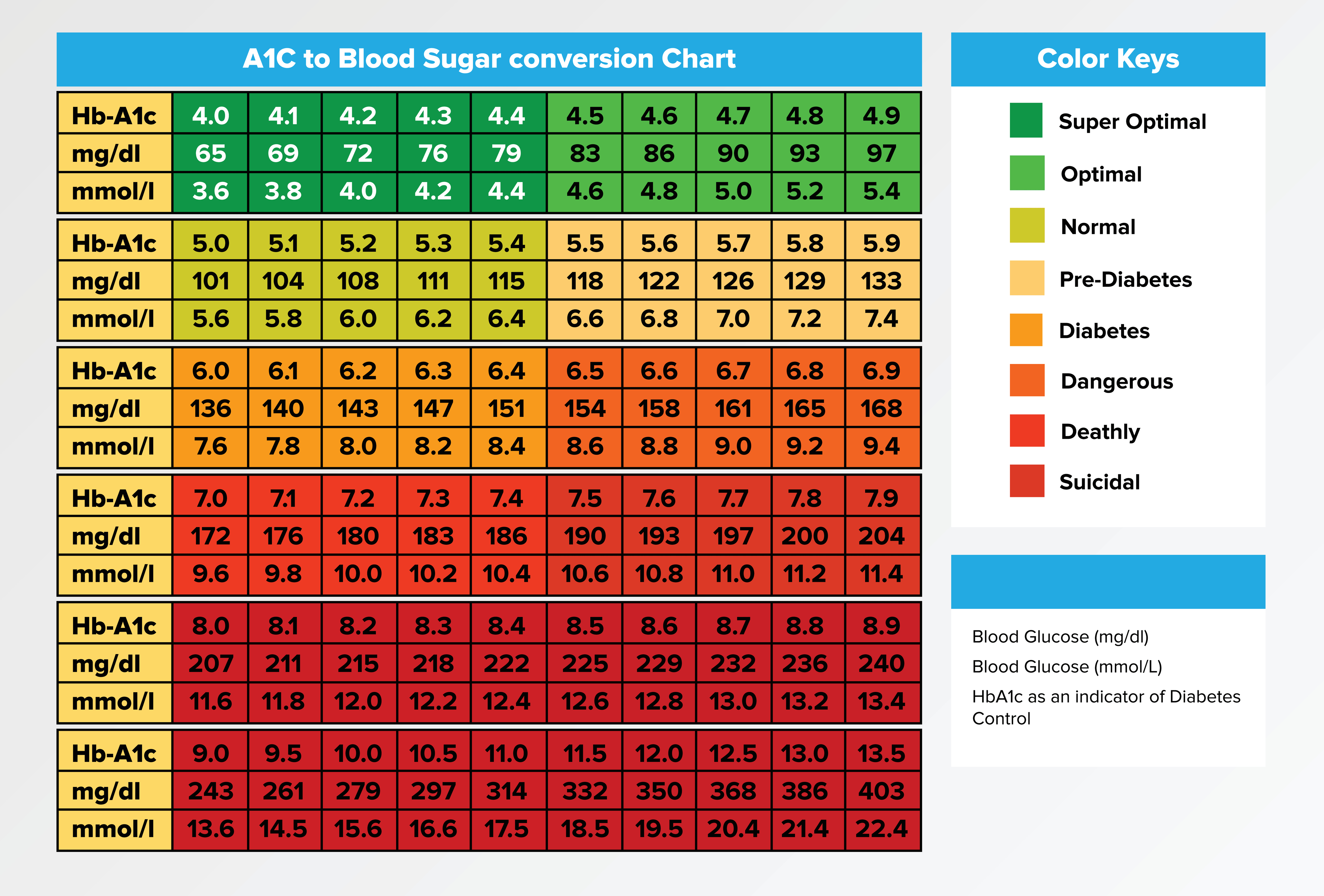
Know What A1c Test Measures, Conversion Calculator, Ranges & Tips Breathe WellBeing
A1c Blood Glucose Conversion Chart Type One Diabetic A1c C
A1c Blood Glucose Conversion Chart Type One Diabetic A1c C
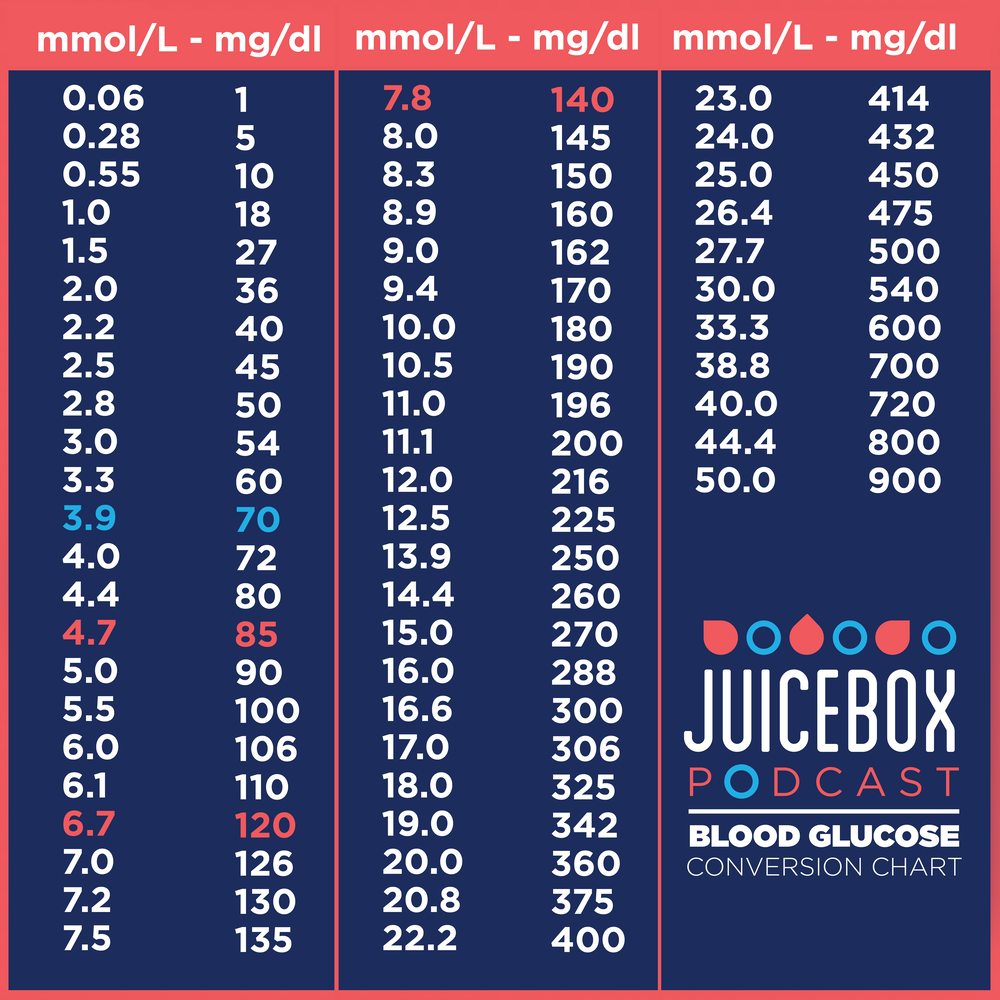
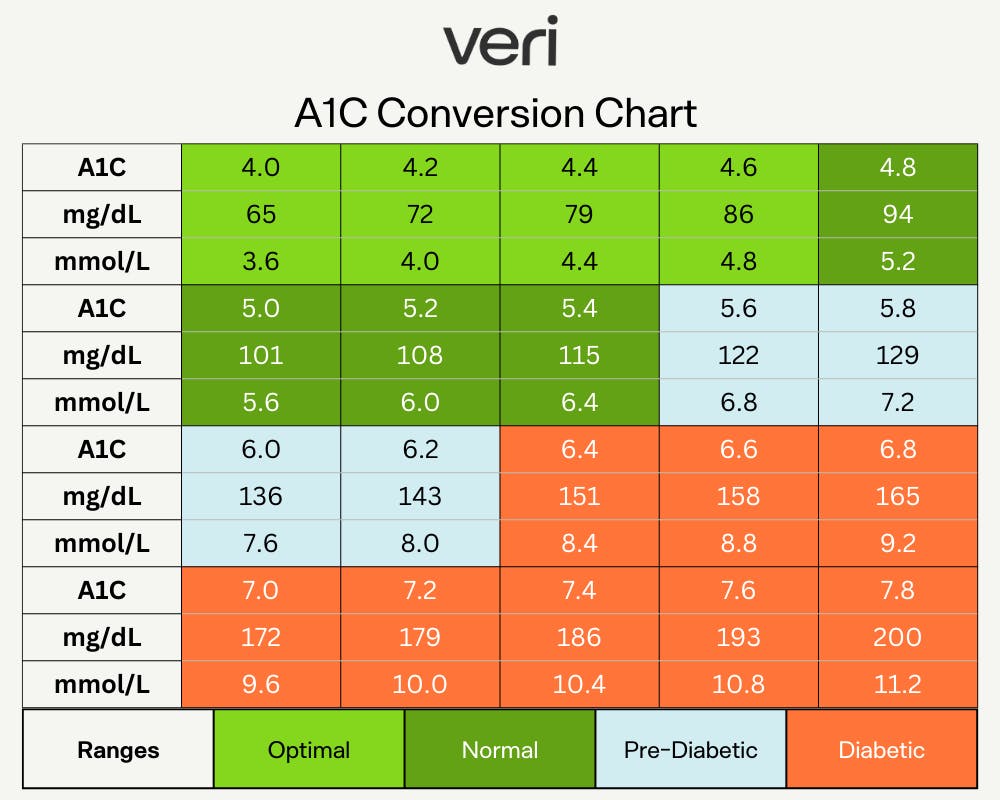
Blood Sugar Conversion Chart and Calculator Veri
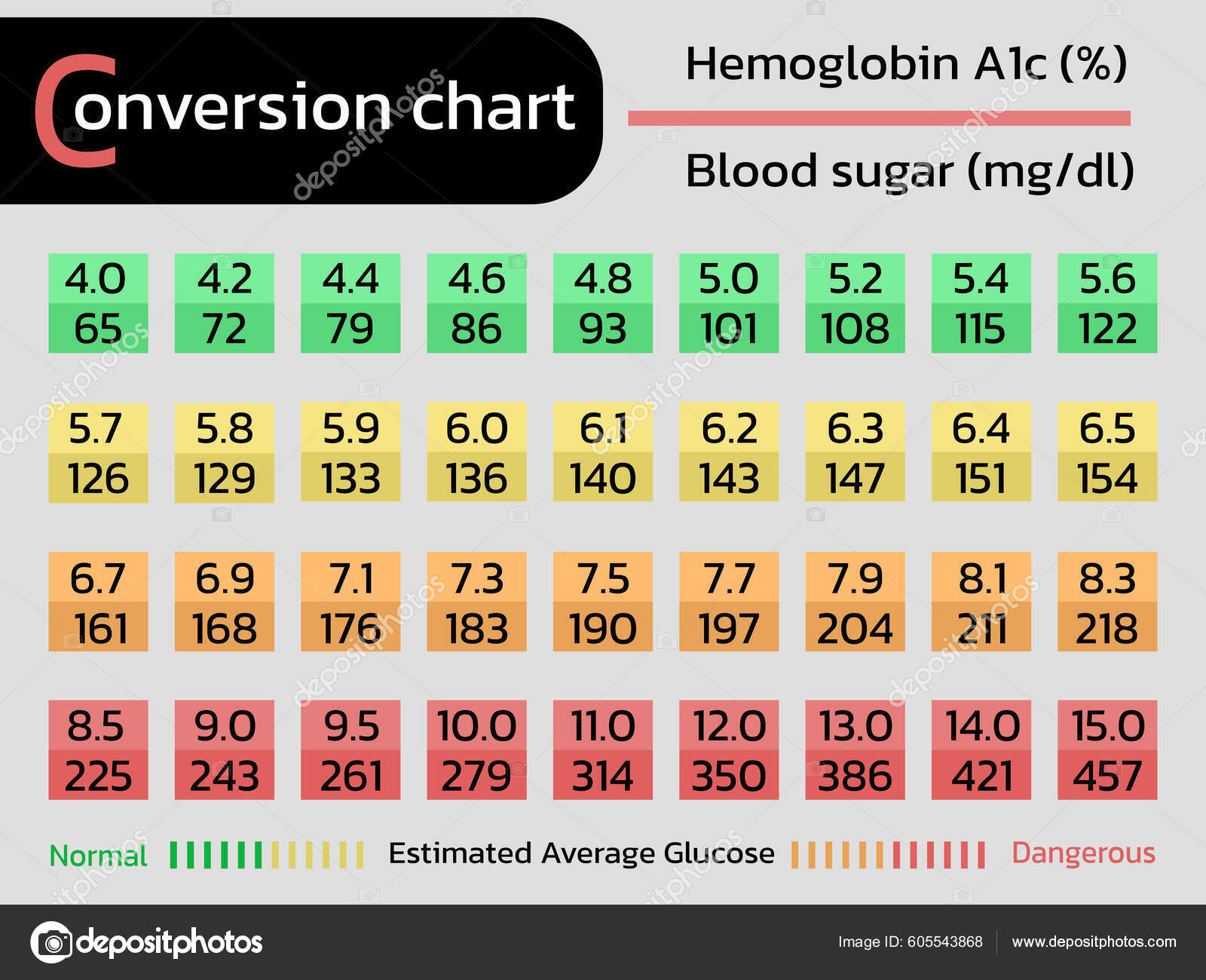
Conversion Chart Hemoglobin A1C Glucose Stock Vector Image by ©kohyaotoday 605543868
There Are 2 Ways To Do It.
It Comes From The Food You Eat.
Carbohydrates Are Ubiquitous Energy Sources For Every Organism Worldwide And Are Essential.
Glucose Is The Body’s Main Source Of Energy.
Related Post: