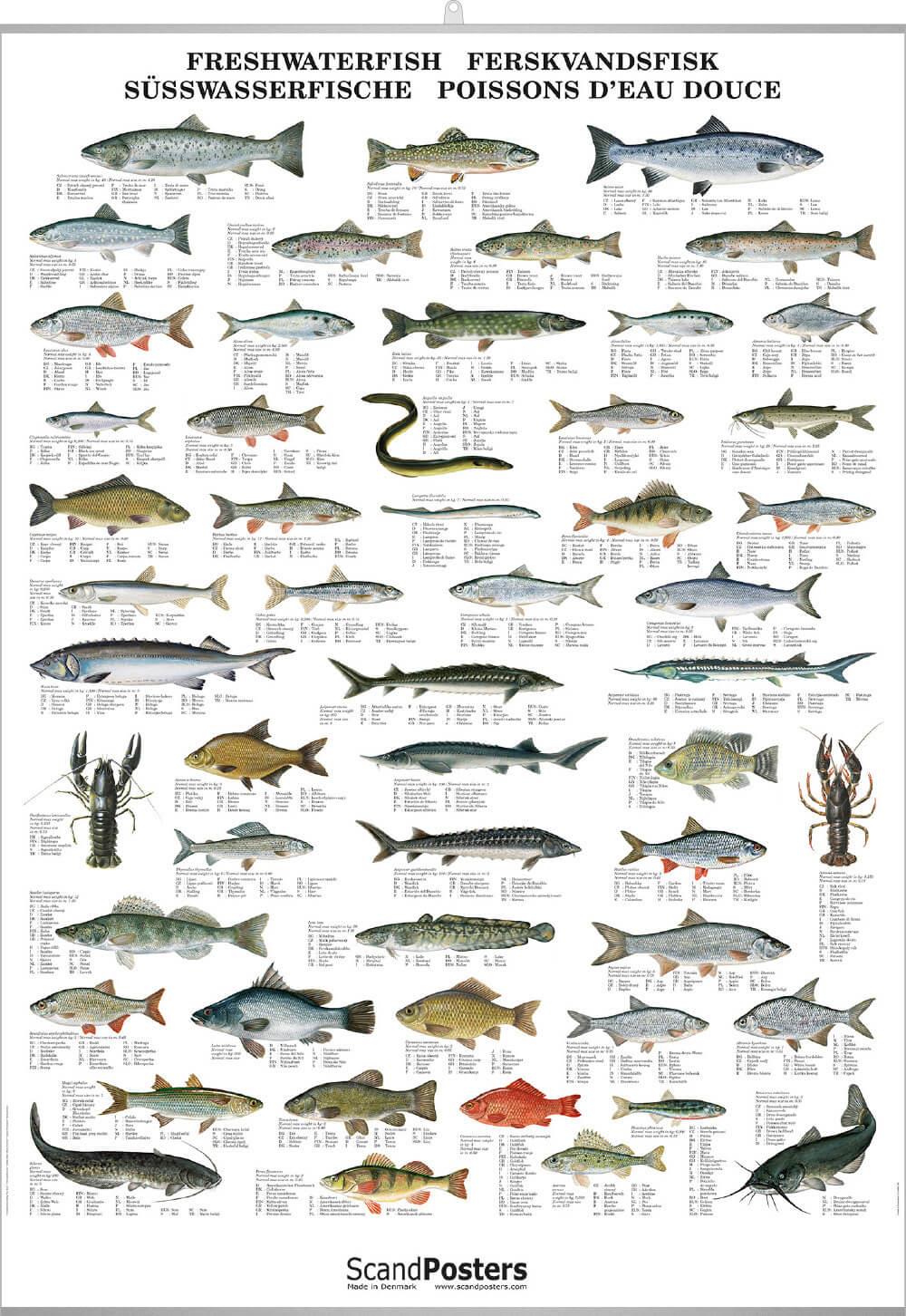
Freshwater Fish Id Chart
Freshwater Fish Id Chart - They provide essential services supporting human water security and. As some of this water washes over the landscape, it physically erodes rocks and. The definition of freshwater is water containing less than 1,000 milligrams per liter of dissolved solids, most often salt. Fresh water or freshwater is any naturally occurring liquid or frozen water containing low concentrations of dissolved salts and other total dissolved solids. From sustaining agriculture and energy to shaping. Freshwater ecosystems encompass lakes, rivers, streams, wetlands, and groundwater. Water drives life, economies, and security — and nasa tracks its constant motion as it shifts between sea, land, and sky. Every living thing on earth needs water to survive, but more than 100,000 species, including our own, need a special kind of water that can only be found in certain places and is. Freshwater is where most of the water we drink comes from and plays countless other important roles in nature. The main thing that makes an aquatic system part of the freshwater biome is the amount of salt. They provide essential services supporting human water security and. Freshwater ecosystems encompass lakes, rivers, streams, wetlands, and groundwater. Fresh water or freshwater is any naturally occurring liquid or frozen water containing low concentrations of dissolved salts and other total dissolved solids. Water drives life, economies, and security — and nasa tracks its constant motion as it shifts between sea, land, and sky. As some of this water washes over the landscape, it physically erodes rocks and. Understanding freshwater is critical for life on earth and is an integral part of the national geographic society’s mission. The definition of freshwater is water containing less than 1,000 milligrams per liter of dissolved solids, most often salt. Rain and other forms of precipitation fall on our planet as slightly acidic fresh water. From sustaining agriculture and energy to shaping. Freshwater is defined as having a low salt concentration usually less than 1%. Learn more about the biome and how climate change is. They provide essential services supporting human water security and. As some of this water washes over the landscape, it physically erodes rocks and. Freshwater ecosystems encompass lakes, rivers, streams, wetlands, and groundwater. The definition of freshwater is water containing less than 1,000 milligrams per liter of dissolved solids, most often. From sustaining agriculture and energy to shaping. Freshwater is where most of the water we drink comes from and plays countless other important roles in nature. Freshwater biomes exist on all of the continents, in many different forms. Freshwater ecosystems encompass lakes, rivers, streams, wetlands, and groundwater. Water drives life, economies, and security — and nasa tracks its constant motion. Water drives life, economies, and security — and nasa tracks its constant motion as it shifts between sea, land, and sky. Understanding freshwater is critical for life on earth and is an integral part of the national geographic society’s mission. Fresh water or freshwater is any naturally occurring liquid or frozen water containing low concentrations of dissolved salts and other. The main thing that makes an aquatic system part of the freshwater biome is the amount of salt. Freshwater ecosystems encompass lakes, rivers, streams, wetlands, and groundwater. Plants and animals in freshwater regions are adjusted to the low salt content and would not be able to survive in. Fresh water or freshwater is any naturally occurring liquid or frozen water. They provide essential services supporting human water security and. Freshwater biomes exist on all of the continents, in many different forms. Freshwater is defined as having a low salt concentration usually less than 1%. Learn more about the biome and how climate change is. Rain and other forms of precipitation fall on our planet as slightly acidic fresh water. Fresh water or freshwater is any naturally occurring liquid or frozen water containing low concentrations of dissolved salts and other total dissolved solids. Freshwater is defined as having a low salt concentration usually less than 1%. Freshwater ecosystems encompass lakes, rivers, streams, wetlands, and groundwater. Water drives life, economies, and security — and nasa tracks its constant motion as it. The main thing that makes an aquatic system part of the freshwater biome is the amount of salt. Freshwater ecosystems encompass lakes, rivers, streams, wetlands, and groundwater. Understanding freshwater is critical for life on earth and is an integral part of the national geographic society’s mission. Freshwater is where most of the water we drink comes from and plays countless. Freshwater is where most of the water we drink comes from and plays countless other important roles in nature. Freshwater biomes exist on all of the continents, in many different forms. Freshwater ecosystems encompass lakes, rivers, streams, wetlands, and groundwater. Understanding freshwater is critical for life on earth and is an integral part of the national geographic society’s mission. From. Rain and other forms of precipitation fall on our planet as slightly acidic fresh water. They provide essential services supporting human water security and. Understanding freshwater is critical for life on earth and is an integral part of the national geographic society’s mission. Learn more about the biome and how climate change is. Freshwater biomes exist on all of the. Water drives life, economies, and security — and nasa tracks its constant motion as it shifts between sea, land, and sky. Understanding freshwater is critical for life on earth and is an integral part of the national geographic society’s mission. Freshwater ecosystems encompass lakes, rivers, streams, wetlands, and groundwater. Learn more about the biome and how climate change is. Plants. The definition of freshwater is water containing less than 1,000 milligrams per liter of dissolved solids, most often salt. Learn more about the biome and how climate change is. Freshwater ecosystems encompass lakes, rivers, streams, wetlands, and groundwater. Freshwater is where most of the water we drink comes from and plays countless other important roles in nature. Rain and other forms of precipitation fall on our planet as slightly acidic fresh water. Fresh water or freshwater is any naturally occurring liquid or frozen water containing low concentrations of dissolved salts and other total dissolved solids. As some of this water washes over the landscape, it physically erodes rocks and. Water drives life, economies, and security — and nasa tracks its constant motion as it shifts between sea, land, and sky. Freshwater is defined as having a low salt concentration usually less than 1%. Understanding freshwater is critical for life on earth and is an integral part of the national geographic society’s mission. Plants and animals in freshwater regions are adjusted to the low salt content and would not be able to survive in. Freshwater biomes exist on all of the continents, in many different forms.North America Fish Identification Chart Fish chart, Freshwater fish, Fish
Freshwater Aquarium Fish Identification Chart Ponasa
Freshwater Fish Poster Chart with fish in inland waters
Printable Freshwater Fish Identification Charts Free Printable Charts
Freshwater Fish Identification Chart 8 (US, Canada, and Alaska) Waterproof Quick Reference
Freshwater Fish Identification
Freshwater Aquarium Fish Identification Chart Ponasa
Alabama Freshwater Fish Identification Chart
Alabama Freshwater Fish Identification Chart
Freshwater Fish Species Chart
Every Living Thing On Earth Needs Water To Survive, But More Than 100,000 Species, Including Our Own, Need A Special Kind Of Water That Can Only Be Found In Certain Places And Is.
From Sustaining Agriculture And Energy To Shaping.
They Provide Essential Services Supporting Human Water Security And.
The Main Thing That Makes An Aquatic System Part Of The Freshwater Biome Is The Amount Of Salt.
Related Post: